
Despite record spending on cybersecurity, a new study finds that IT security breaches remain at epidemic levels.
According to a new report conducted by Osterman Research, a whopping 70 percent of the more than 200 medium and large organizations surveyed reported being the victim of at least one successful cyber-attack or data breach in the prior year.
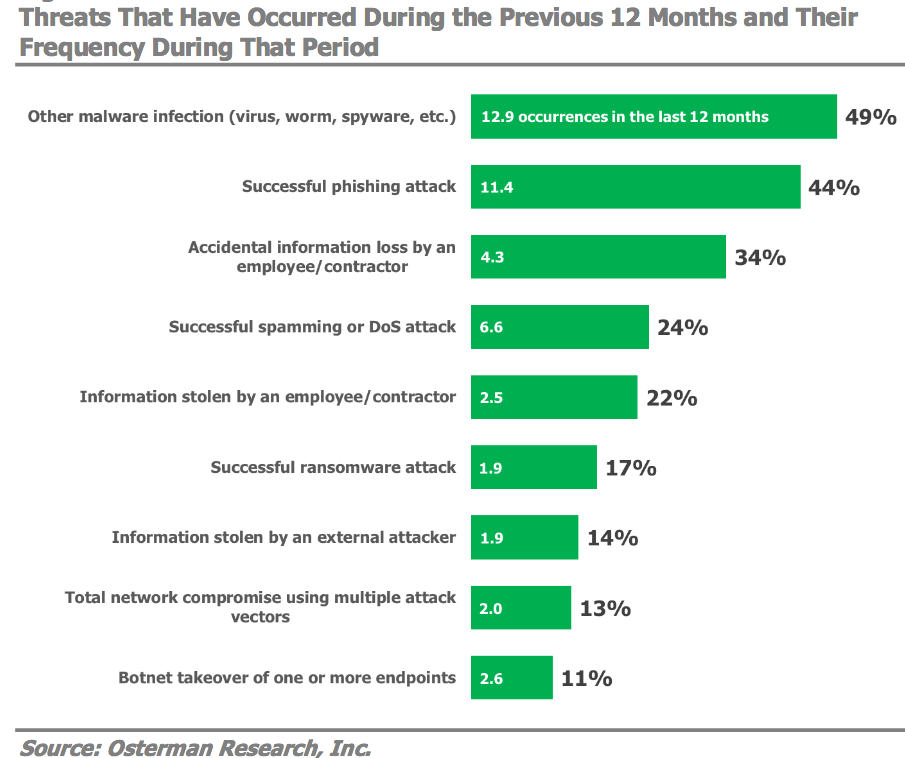
The most common cyber-attack methods were viruses, worms, or other malware infections (49 percent) and phishing attacks (44 percent). Additionally, more than a third (34 percent) said they experienced accidental information loss by employees or contractors, the report found. The study was sponsored by cybersecurity firm Cyren.
Biggest IT Threats
IT and security professionals surveyed said they were either highly concerned or extremely concerned about the following cyber-threats, the report found:
- Ransomware attacks (67%)
- A breach of sensitive or confidential data (66%)
- Phishing attacks (62%)
- Malware infiltration through HTTPS/SSL web traffic (54%)
- Targeted attacks/zero-day exploits (54%)
- Shadow IT/employees using unauthorized cloud apps and services (48%)
- Endpoints compromised by botnets (46%)
- Cryptocurrency mining malware being installed on internal PCs or servers (45%)
- Use of CPU by cryptocurrency miners when users visit websites (38%)
- Employees surfing websites that violate company policies (36%)
Gone Phishing
Among the most alarming results of the survey is the success that attackers are having with phishing attacks, despite increased spending and efforts to prevent them. A full Forty-four percent of organizations reported they suffered a successful phishing attack, up from 30 percent in 2017. The average number of total successful phishing attacks over the prior year reported by these organizations was 11.4.
The success in phishing attacks comes despite vigorous efforts to defend against them. More than nine out of ten companies surveyed said they conducted phishing awareness training for employees and executives.
“Business IT decision-makers clearly need to take a fresh look at their security in order to combat the rising tide of phishing,” Michael Osterman, principal analyst of Osterman Research, said in a press release.
Cybersecurity Spending on the Rise
The rise in cyber-attacks also comes despite an increase in overall spending on cybersecurity. IT security spending in the United States continues to rise rapidly, with 49 percent reporting increased security-related costs by an average 18 percent over the prior year. None of the respondents reported a decrease in such spending.
The results of the survey indicate that IT security professionals might need to seek some new solutions to address cybersecurity threats. “The solutions that are in place to prevent problems from things like shadow IT, malicious insider activity, or targeted spoofing or impersonation of emails are not working so well,” the report states.
There were few bright spots in the survey results, but the report did identify two areas where progress is being made:
- Sixty-two percent of those surveyed this year believe that their security solutions that address malware infiltration through HTTPS/SSL web traffic are working well or very well compared to only 44 percent last year.
- Solutions that address ransomware are faring better in this year’s survey than last year’s (50 percent to 44 percent).
Yet even if some types of attacks are declining slightly, the results indicate that their severity is not declining. According to the report, “some types of successful attacks are experienced less, but can have extremely serious consequences. Seventeen percent reported suffering a successful ransomware attack,” for example, “and 13 percent suffered a “total network compromise” using multiple attack vectors.” ![]()

